Whether you're white hat, black hat, or some shade in-between, navigating through a network is a core part of hacking. To do that, we need to be able to explore a network to discover the addresses of gateways, interfaces, and other attached devices. When ifconfig just isn't enough, you can steer your way around a network with a convenient tool called Ship, the script for everything IP.
What Is Ship?
Created by Sotirios Roussis, Ship is a portmanteau of "shell" and "IP" and it's literally a shell script that displays network addresses. However, that description doesn't really give it justice. Ship is a very handy tool. I like to think of it as a one-stop-shop for basic network reconnaissance and addressing.
Ship can display everything from the gateway IP address to the IP and MAC addresses of all the active devices on a network. It can do simple things like ping and traceroute, as well as more sophisticated things like listening in on ports and calculating binary and hex information about an IP. The command syntax in Ship is simple and straightforward, and I recommend it to everyone who finds themselves poking around Wi-Fi networks via terminal on a regular basis.
Step 1: Downloading & Installing Ship
In this tutorial, I'm using Black Arch Linux, so the commands may be slightly different if you're using Kali or another Linux distribution.
Depending on what repositories your package manager checks, you might be able to install Ship directly with a simple apt-get or equivalent command. On my system, this wasn't the case, so I'm going to detail how to install Ship manually.
First, we need to install the appropriate dependencies. To do this, use the following command in Black Arch.
pacman -S gawk grep iproute2 mtr iputils sed traceroute wget
If you're using a Debian-based system like Kali, this command should work the same if you replace pacman -S with apt-get install and iputils with iputils-ping.
In my case, all of these packages were already installed, but it doesn't hurt to check. If you already have them installed like I did, the command will update them instead, which is always a good thing.
After we install the dependencies, we need to clone the GitHub repository. I chose to do this in the root directory of my Linux system, so it will be downloaded into /root/ship. Use the following command in a terminal window to download Ship directly from GitHub.
git clone --branch=master https://github.com/xtonousou/ship.git
This will download the ship.sh shell file into /root/ship. As is, we won't be able to call Ship simply by typing ship into the terminal. To do this, navigate to Ship's directory with cd /root/ship and then copy ship.sh and rename it to ship by typing cp ship.sh ship into a terminal window.
This lets us type ship instead of having to type ship.sh. Then, to add it to the PATH variable everytime the terminal runs, by typing:
echo 'export PATH=/root/ship:$PATH'>>~/.bashrc
Step 2: Using Ship for Quick Addressing
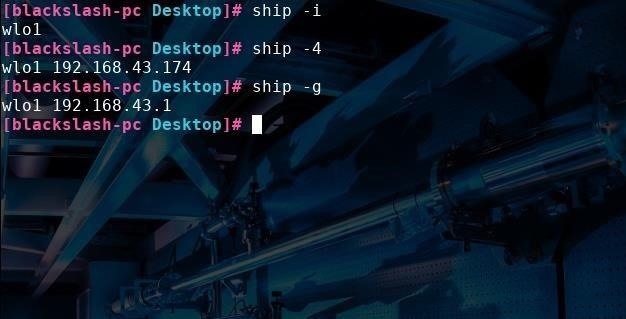
Now that we've installed Ship, let's browse some of its features. One of Ship's most handy uses is that it can quickly serve up the exact information about the network we need without displaying superfluous information. For instance, if all we want is to find just the name of the active network interface connected to our device, type ship -i.
You can see in the picture below that my laptop's internal wireless adapter is called wlo1. If we also want that interface's IP address, type ship -4 or ship -6 for IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, respectively. We can also find the internal (private) IP address of the network gateway by typing ship -g.
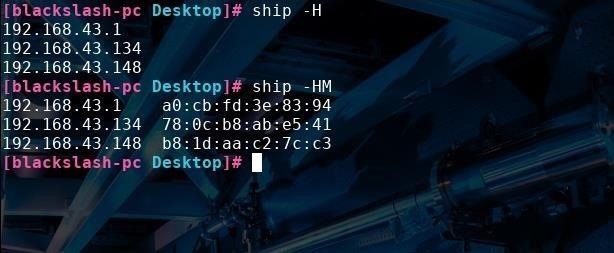
So far, this is all stuff we can easily access already with ifconfig or ip a, although for convenience, Ship will display this information more concisely. But let's move on to some cooler stuff Ship can do, like quickly displaying all the devices on the current subnet. Type ship -H or ship -HM (to also display a device's corresponding MAC address) and you'll see a table of all active network hosts, like in the picture below.
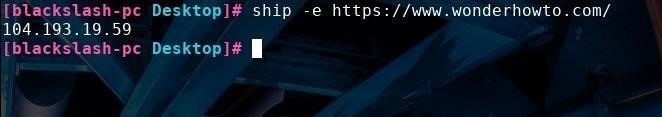
In addition, you can quickly see what your external IP address is by typing ship -e. You can also use this same command with a URL to find the IP address associated with website by typing ship -e url, with "url" replaced by the site you want the IP address of.
Step 3: Port Listening with Ship
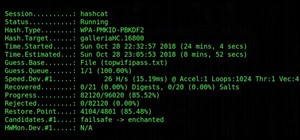
Ship can also show real-time information on all the external IP addresses you are connecting to on a specific port. By typing ship -p portNumber, Ship will display a table of counts and IP addresses that updates every few seconds. In the screenshot below, I tested this on port 80, displaying all active port connections.

All the IP addresses to the right are outgoing connections through port 80. We can see a connection to Google if we look up the last IP address (216.58.193.206) in a browser, as it redirects to Google.com.
Step 4: Calculating IP Information
If you need to convert an IP address into binary or hexadecimal, you can type the ship -c address command. This will also display a plethora of other information for you, including the subnet mask, the class of network associated with the address, and the maximum amount of hosts that network can support.
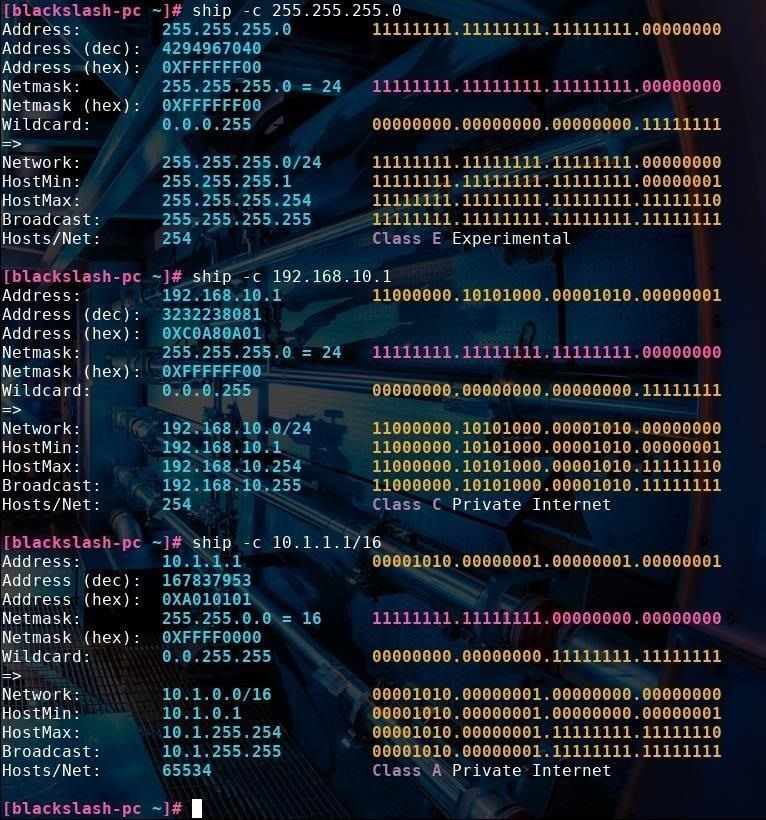
I tried using this command with multiple different IP addresses of various classes. Ship labels whether the IP address belongs to a private network and whether it belongs to class A, B, C, D, or E.
One thing to note is that you can use this command with CIDR notation. For instance, when I type 10.1.1.1/16, it correctly calculates the network mask to be 255.255.0.0 and the max number of hosts to be 65,534, as opposed to the standard 255 in a normal class C 198.192.x.x/24 type network. This can tell us a lot about the purpose of the network we're examining.
Ship Can Answer Network Questions
If you're new to networking or need to navigate through an uncharted network, Ship is like a compass to show you what's out there and how to get where you want to go. With a few simple commands, even a beginner can discover connected devices and quietly gather information about a network and the way it is administered. Ship makes it easy to find the network information you need for other commands, down to the driver being used by each network interface.
Keep in mind, Ship organizes other tools that do the behind the scenes work. Some of these tools can leave logs in the router, firewall, or intrusion-detection system. While scanning generally isn't illegal, it's often seen as a preparation for an attack and can get you blocked from a well-defended network.
If you have any questions, you can comment below or ask me on Twitter @blackslash6.
Just updated your iPhone? You'll find new emoji, enhanced security, podcast transcripts, Apple Cash virtual numbers, and other useful features. There are even new additions hidden within Safari. Find out what's new and changed on your iPhone with the iOS 17.4 update.



















10 Comments
Tried all your instructions on Parrot Security (Debian based) and I still cannot call this application from terminal. Any suggestions are appreciated.
navigate to the ship/ship directory using cd
rename and copy file: cp ship.sh /usr/bin/ship
set permissions: chmod 777 /usr/bin/ship
Where is the file located and is that location in $PATH. It's a shell script so if you didn't miss any steps it should work. I use parrot and it works fine. Need a little more info than that it's not working to figure it out. What did you do exactly? what folder is it in and did you change the permissions to execute it?
command apt-get install gawk grep iproute2 mtr iputils-ping sed traceroute wget its not working in kali linux .so is there anything that i need to change
Kali should already have most those packages installed. but if you are having issue installing to Kali you may need to install the kernel headers for Debian since Kali is built upon it. You may also try to download and use dpkg -i on the package directly, http.kali.org/kali/pool/main/i/iproute2/ , keep in mind there maybe dependencies needed.
Now lets do some simple testing issue these command as root no sudo:
apt-cache search iproute2
apt-get update
apt-get install iproute2 iproute2-doc
This may take care of your issue assuming your Kali version is not outdated.
Hope this helps.
For those getting "unrecognized command" error, here is what I did to solve it.
Restart terminal.
Enter "cd ship"
Then enter "chmod 777 ship"
I think this is not worth, Instead we can use nmap and traceroute to find those informations....., and it also not efficient as nmap and other tools
Step 1:
Everything worked for me. However, when i type in "ship -i", it says "bash: /root/ship/ship: Permission denied". Where did I go wrong? Can someone help please?
use chmod 777 /root/ship/ship to get permission
Good morning,
i have a couple questions to ask you. Which version of Rasbery pi would you suggest? For learning Ethical Hacking
What parts do i need to buy. if i want to learn ethical hacking?
Where would i buy them? how much would they cost me.
Any cheap sites that you would recommend?What kind of monitor, keyboard,mouse do i need that would work with Rasbery pi?
Share Your Thoughts